Basics of SEO
Chapter 1
Do you feel that SEO is too hard and not worth the effort?
SEO isn’t that complicated. It’s quite simple—or at least the basics are. But the basics aren’t enough to get you ranked, right?
Wrong.
Here’s the truth:
Most people who run websites have a limited understanding of SEO, so you often only need to get the basics right to succeed.
In this post, you’ll learn the five fundamental steps to SEO success:
- How to figure out what your customers are searching for
- How to optimize your web pages for your target keywords
- How to make sure your website is accessible to both search engines and humans
- How to get other websites to link to your site, and finally:
- How to start measuring your SEO success
I’ve made every effort to keep this as jargon-free as possible without scrimping on actionability.
Prefer something a little more succinct in video format? Try this:
Without further ado, let’s get started.
Step 1: Learn what your customers are actually searching for
You can’t optimize your website without knowing what your customers are searching for—that much is obvious.
How do you figure this out? The best starting point is to use common sense.
Imagine that you run a hotel in Dublin, Ireland. It doesn’t take an SEO genius to guess that your customers are probably searching for things like:
- ‘hotels in Dublin’
- ‘place to stay in Dublin’
- ‘accommodation in Dublin’
Before you do anything else, think about what your customers might be searching for and jot your ideas down in a notepad. You could even ask them directly.
No need to go overboard here—a handful of ideas will do.
Done? Good. Let’s do some more research.
a) Figure out the most popular way people search for your business
It’s likely that some of your customers are searching for your business using the words and phrases you jotted down. Whether the majority of people are is another story.
So the first step is to figure out the most common way people search for what you do.
You can use the ideas you’ve already jotted down to do that. Start by doing a Google search for one of the words or phrases on your list. It doesn’t matter how ridiculous or long-winded this phrase is. I’ll use a purposely silly one to prove it.
Here are the top few search results for that query:
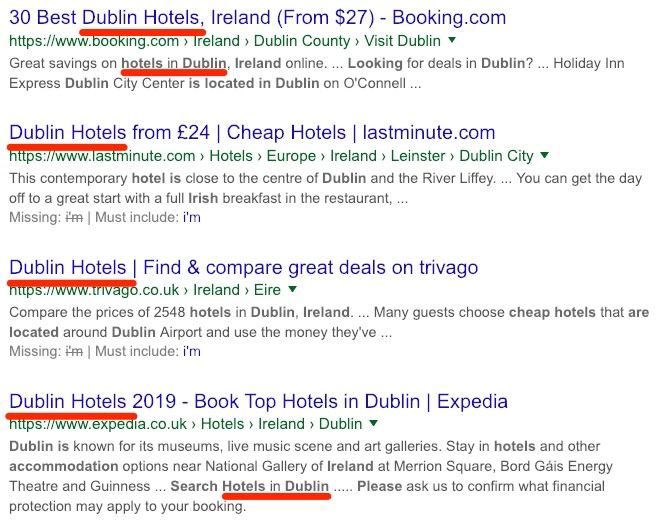
Having skimmed these results for all of 10 seconds, I can see they each have the phrase “Dublin hotels” in the title.
This matters because websites tend to optimize their title tags for SEO, so it’s likely that these particular ones have already done some research and found that “Dublin hotels” is the most popular way people search for places to stay in Dublin.
But let’s not get ahead of ourselves.
There’s no guarantee that these folks know what they’re doing.
Let’s make sure this is a good main keyword to target by checking out our original search term in Ahrefs Keywords Explorer.
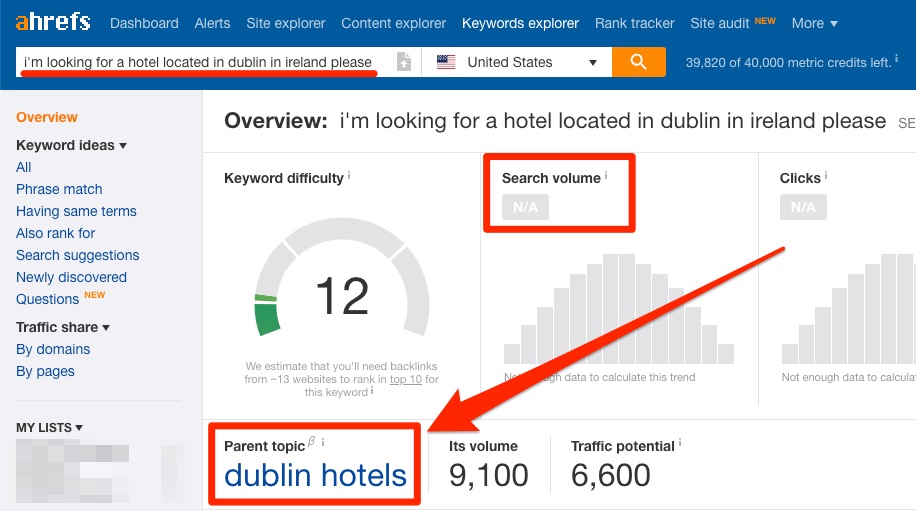
Bingo. When we search for the same phrase in Keywords Explorer, it tells us that the Parent topic is “Dublin hotels” with a monthly US search volume of 9,900. It also has good traffic potential.
This confirms our initial suspicions that this is a good main keyword to target.
b) Understand other ways people may be searching for the same thing
Let’s take a look at the SERP overview for “Dublin hotels” in Keywords Explorer.
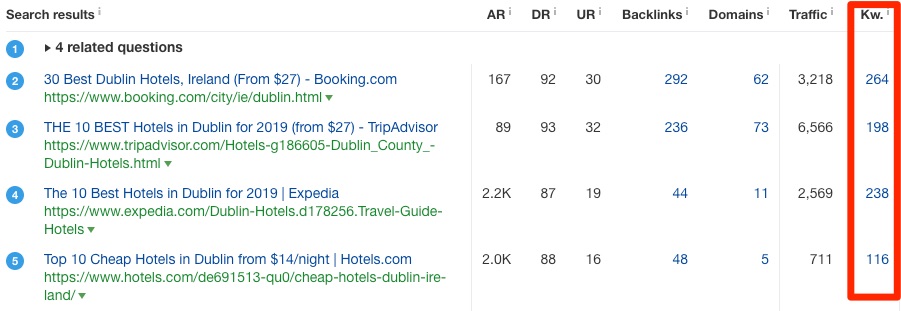
Take note of the “Kw.” column, which shows how many keywords for which each of the top 10 web pages rank.
The average here is around 150–200 keywords.
In other words, each of these web pages gets traffic from hundreds of other long-tail and related keywords. That means not everyone types “Dublin hotels” into Google when searching for a place to stay in Dublin. Other people search for the same thing in different ways.
You can start to get a sense of what these other keywords are by analyzing more Google search results.
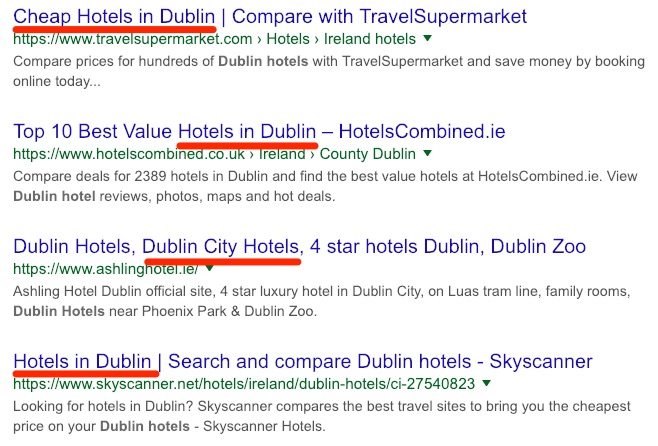
Look for more similar and related phrases that pop up over and over again.
In this instance, we see such phrases as “hotels in Dublin,” “Dublin city hotels,” and “cheap hotels in Dublin.”
These businesses have likely identified these keywords and phrases already, hence the reason they include them in their title tags.
If you want even more suggestions, try the Also rank for report in Keywords Explorer.
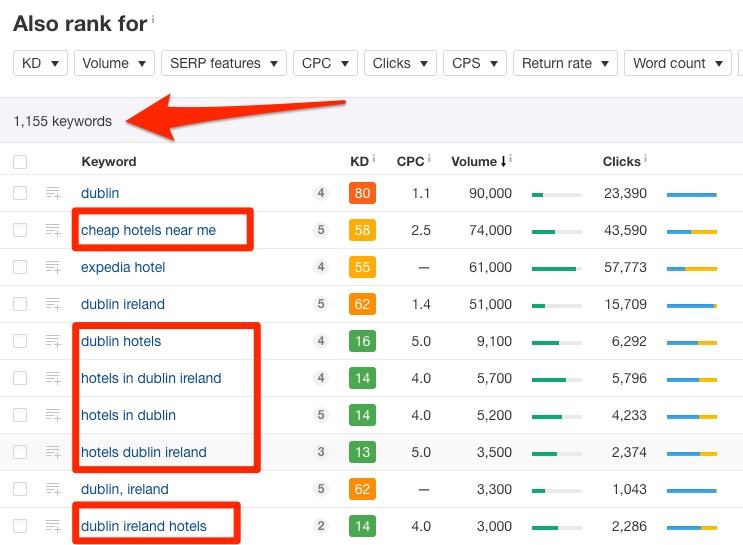
This report shows the keywords for which the top 10 ranking pages also rank.
However, this report tends to surface a lot of keywords, which can be overwhelming.
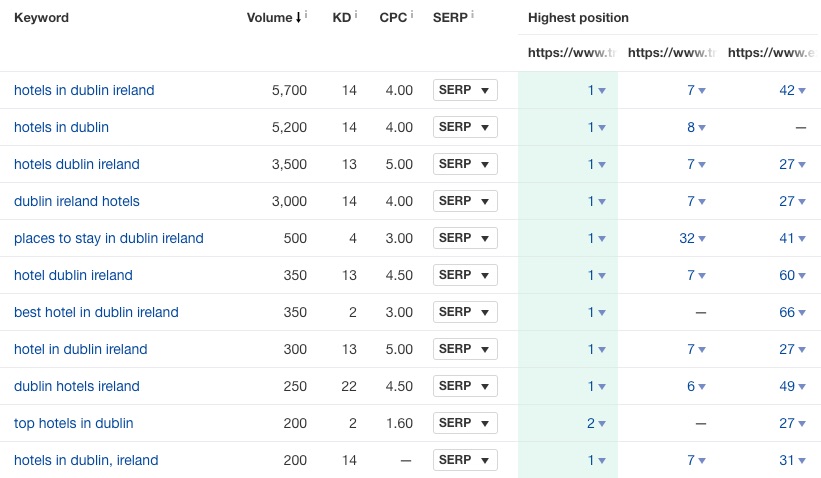
One way to narrow things down to only super relevant results is to take the 2–3 most relevant top ranking pages and paste them into Ahrefs Content Gap tool. That will unveil the common keywords for which all of those pages rank.
c) Delve deeper into the more granular searches your customers are making
Now that you know how people search for your business, it’s time to delve deeper into the more granular searches people make in relation to what you do.
A simple way to start is to look at Google autocomplete results.
Go to Google and begin typing a query in the search box, but don’t hit Enter. Google will immediately suggest some additional search terms that people have used:

You can repeat this step and get more results by adding each letter of the alphabet:

If you’re interested in learning the questions people ask (and search for), check if there’s a “People also ask” box in the Google results…
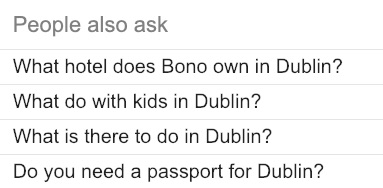
d) Find popular and engaging topics in your field
Content marketing is the art of creating useful and valuable content to attract your target customers or clients. But don’t just start a blog and hope for the best—figure out what topics are popular and engaging in your field and create content related to said topics.
For this, I’d recommend starting with Reddit.
Find a subreddit related to your industry (e.g., r/irishtourism). Look at what people are talking about and which threads are the most popular. You can even filter and sort by the top threads of all time.
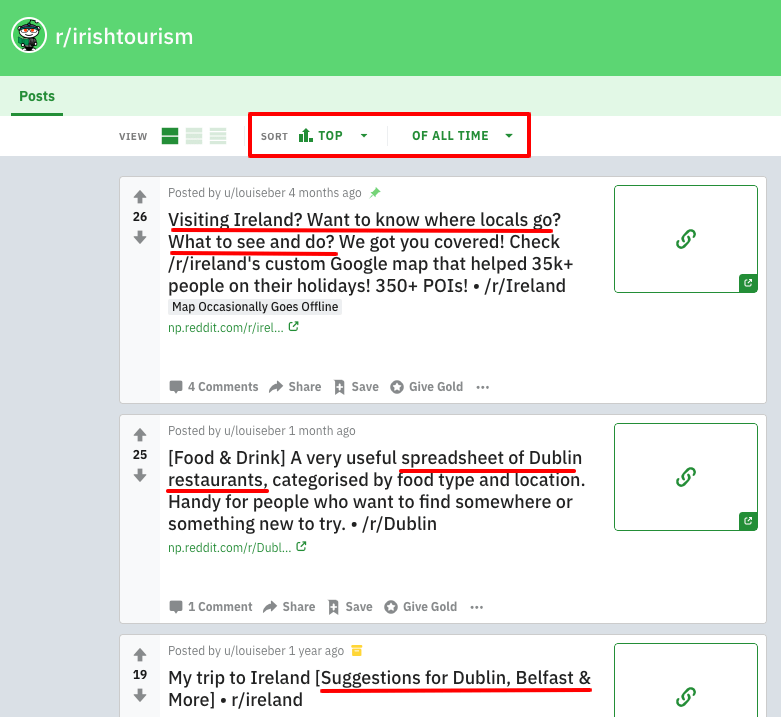
On r/irishtourism, guides and resources about things to do and places to eat and drink are very popular with folks interested in traveling to Dublin.
Want to take things a step further?
Enter Content Explorer.
Content Explorer provides one of the quickest and most reliable methods to understand the most popular and engaging in a given field.
Here’s what I got when I searched for ‘Ireland travel’:
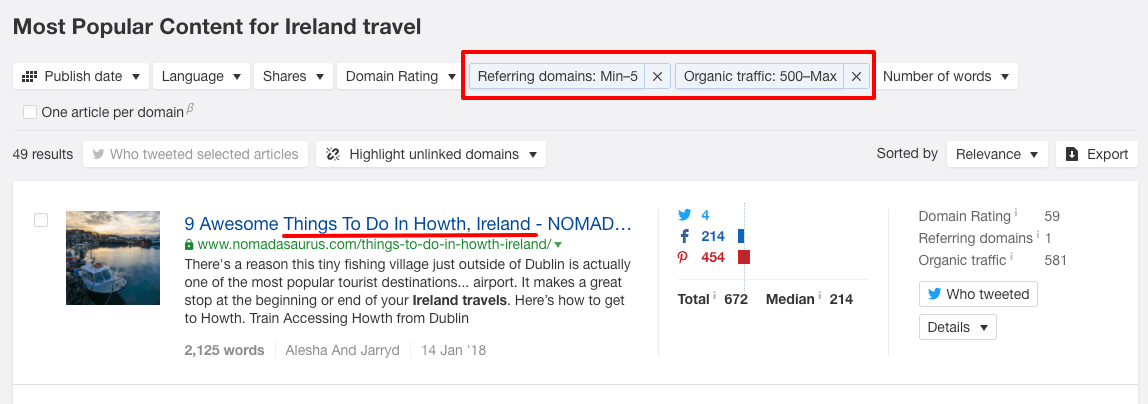
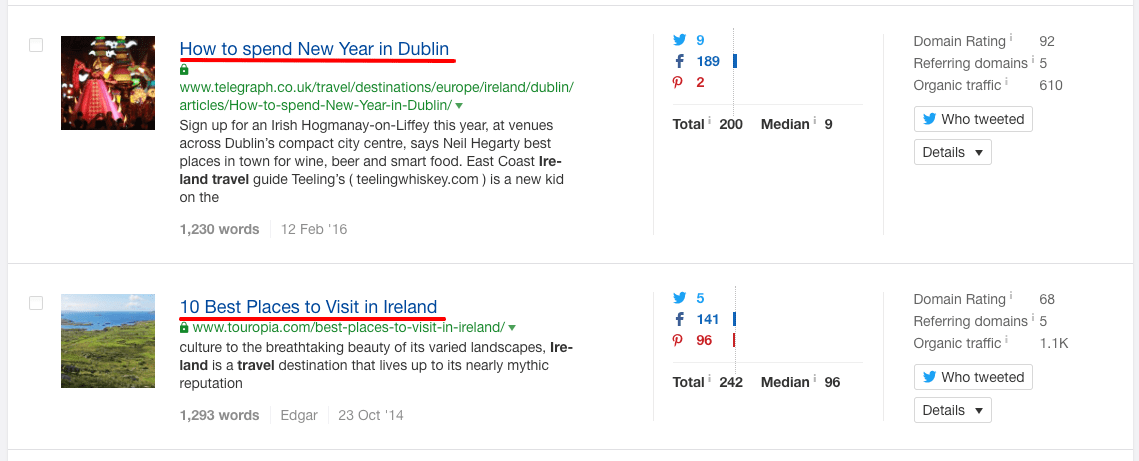
Notice how I used the filters to find pages that get a substantial amount of search traffic even though they only have a handful of links? This allows me to quickly identify relevant popular topics that should be easy to rank for.
I can even see the keywords for which each of these pages ranks by hitting “Details” dropdown.
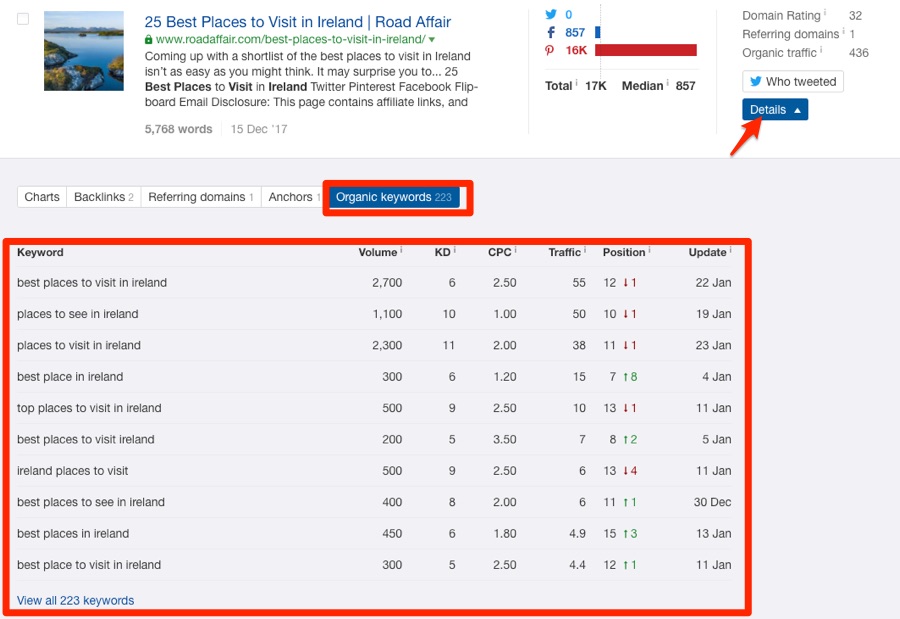
It looks like travel tips are popular. That gives me the idea that we can publish a travel guide to attract visitors and social shares.
Recommended reading: 4 Ways to Find Untapped Keyword Ideas With Great Traffic Potential
e) Expand your keyword list by looking literally anywhere else
Google search results and professional keyword tools can give you a lot to get started with, but it’s in no way enough.
To be successful with SEO, you need to understand how people are talking about the niche you’re operating in, what problems they have, and so on. Use every opportunity to speak to customers and take notice of the language they’re using.
Doing this in person is great, but also very time‐consuming.
So here are a few places where you can find the words people use while talking about your topic of interest:
- Forums: There are quite a few communities where people discuss traveling. For example, a simple search led me to the TripAdvisor Dublin Travel Forum.
- Quora/Reddit: Quora is probably not the first place that comes to mind when you’re looking for travel advice, but you’d be surprised by the amount of information you can find there even on this topic. Where it comes to Reddit, the adage that there’s a subreddit for everything is generally true.
- Facebook/LinkedIn Groups: LinkedIn is more geared towards B2B markets, but when it comes to Facebook, there are groups for almost everything.
Any website or social network with a large number of visitors and user‐generated content can serve as a source of inspiration and keyword ideas.
Podcasts can also be a good source of inspiration…
… as can the contents pages of popular niche-related books on Amazon:
Don’t be afraid to get creative here. Inspiration and keyword ideas are all around you.
f) Understand the metrics behind the keywords you’re targeting
Most people focus entirely on the following two metrics when doing keyword research:
- search volume (the number of monthly searches, on average), and
- keyword difficulty (an estimate as to how easy or hard it will be to appear on the first page of search results for that term).
These are important as they provide useful insights into the potential of the keyword and how difficult ranking for it is likely to be.
However, instead of looking solely at search volume, you should try to figure out the true search traffic potential for each keyword. That way, you can focus your efforts on ranking for the ones that are likely to send the most targeted traffic your way.
In Ahrefs, you can do that by looking at the traffic stats for the current top-ranking pages in the SERP overview in Keywords Explorer:
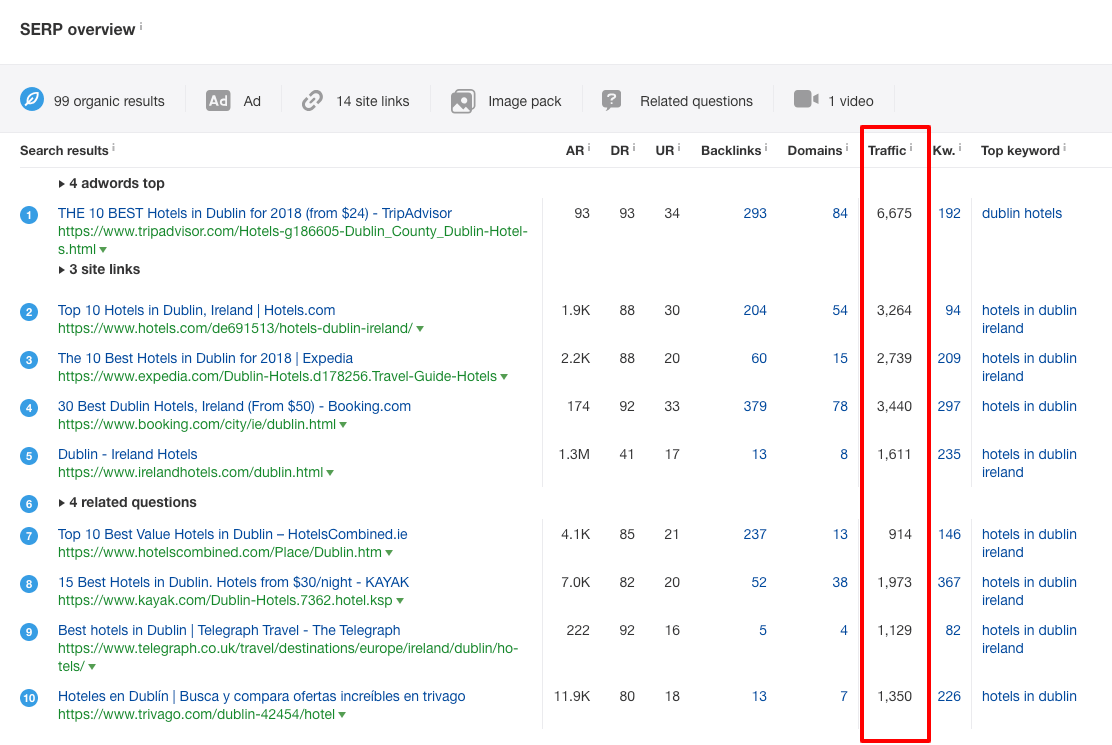
This tells you the estimated total monthly search traffic to each of the top-ranking pages.
You can also see that these pages (which rank for Dublin hotels) also rank for many other related keywords. Looking at these stats gives you an idea of the kind of traffic you can expect to get to your page if you manage to rank.
Note that true traffic potential can significantly exceed the search volume of the keyword you’re researching.
Learn more about keyword research
Keyword research is an essential aspect of SEO, and it can be intimidating to those new to the field. However, understanding the basic concepts and metrics is a must for every website owner who wants more organic traffic.
After you figure out the keywords for which you want to rank and what searchers are expecting to see when they type them in Google, you need to assign those keywords to the pages on your site. It’s worth creating a map (in a spreadsheet or another file) that ties each keyword in your plan to a page on your site.
Chapter 2: Create pages optimized for search
Keyword research is only the first step towards attracting more organic search traffic.
You also need to make sure your pages are structured well and satisfy the person behind the search to rank for the keywords you selected.
Your optimization efforts should start with making sure that your visitors are enjoying the user experience (UX) your website provides. Use design and typography that makes it easy to consume the content, and remove any unnecessary elements such as pop-ups, opt-in boxes, etc. that can annoy your readers.
On‐page optimization is the next step in your SEO strategy.
Even targeting the most profitable keywords with the “best” content won’t help you if your pages are not optimized for search engines.
There are many ways to implement the features I discuss in the following sections, but if you’re using WordPress for your website, I first recommend installing an SEO plugin like Yoast SEO. It’s free and simple to use, and it’s perfect for those who are new to on-page SEO.
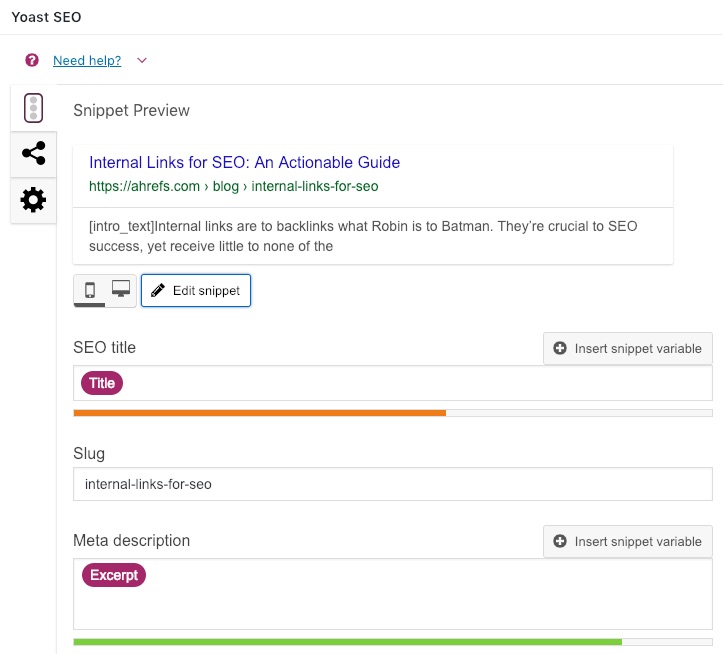
Setting up your pages for success in the search engine involves the following:
a) Create content that aligns with ‘search intent’
Wanting to rank for a keyword doesn’t mean you deserve to, even if your traditional on-page SEO elements are on-point. That’s because of something called search intent.
In short, there are three main ‘types’ of searches people make:
- Navigational: They’re looking for a specific website, e.g., ‘Dublin airport’
- Informational: They’re looking to learn more about a specific topic, e.g., ‘things to do in Dublin’
- Transactional: They’re looking to purchase a specific product/service, e.g., ‘book hotel in Dublin’
Naturally, searches with a high level of commercial interest are more valuable from a business point of view since the people doing them are closer to purchasing (i.e., further down the marketing funnel) and thus more likely to spend money if they land on your site.
But search intent isn’t always crystal clear from the search query itself.
For example, take the query “best hotel in Dublin.”
Now, you might be thinking “my hotel is the best hotel in Dublin, so this is probably a transactional term for which I can rank my homepage,” right? Not so fast.
The best way to understand the intent behind any search term is to see what pages rank for it.
So let’s do that:
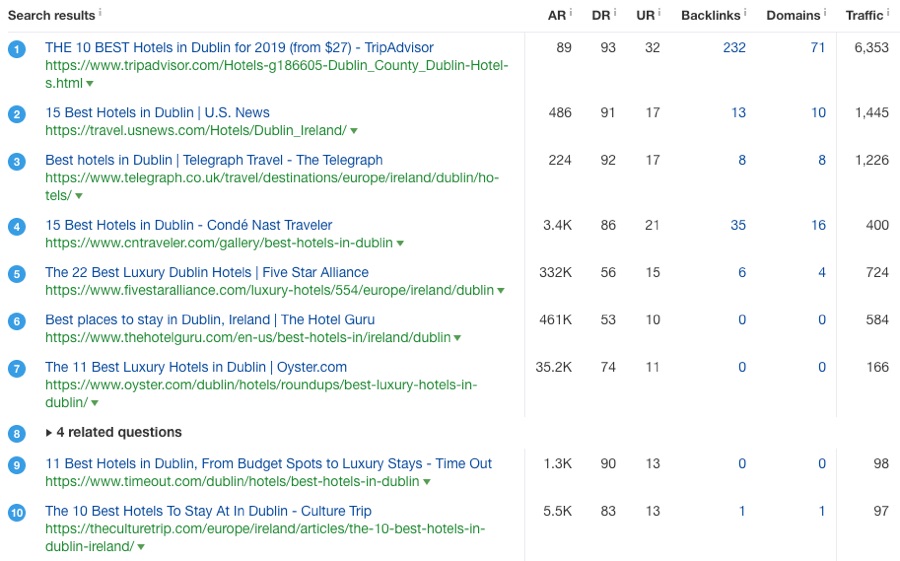
Top 10 ranking pages for “best hotel in Dublin” via Ahrefs Keywords Explorer
Here you can see that almost all of the top-ranking results are blog posts and listicles—i.e., informational results.
The logic here is that because Google’s primary goal is to satisfy its users, their algorithm keeps a close eye on the behavior of people searching for a particular term and tries to offer results that will meet the intent of their search. Thus, you can infer search intent by looking at the commonalities between the current top-ranking pages.
Never create content without first understanding the search intent behind the query you’re targeting.
b) Use short, descriptive URLs
The web address of your page sends a signal to search engines about its topic. Getting this right the first time is recommended because you should avoid changing it, if possible.
Here’s Google’s advice about URLs:
A site’s URL structure should be as simple as possible. Consider organizing your content so that URLs are constructed logically and in a manner that is most intelligible to humans (when possible, readable words rather than long ID numbers).
In other words, don’t go for…
domain.com/56945602_86587356.asp
…when you could go for something descriptive like:
domain.com/dublin-guide
The other benefit of descriptive URLs is that they often include your target keyword (or at least words and phrases from it). That said, don’t shoehorn keywords into URLs if they look unnatural.
c) Create compelling meta titles and descriptions
Web pages have two specific features that search engines use when building up search results:
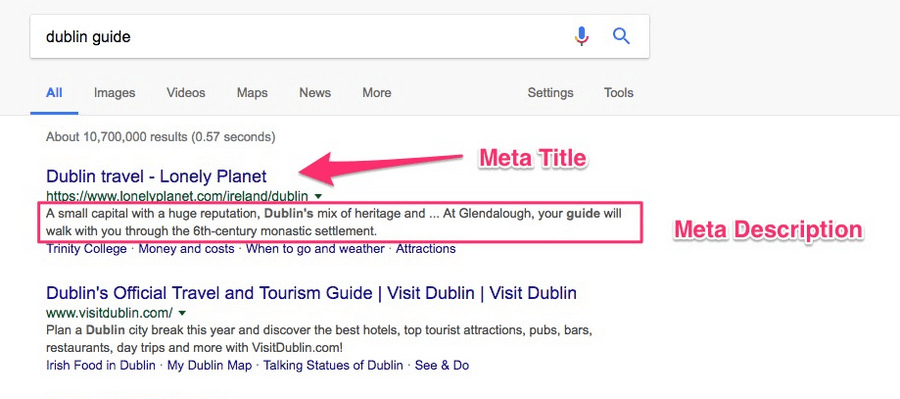
Contrary to what the name suggests, the meta title tag does not appear anywhere on your page. It merely sets the name of the browser tab, and Google and other search engines use it when showing the page in search results.
SIDENOTE.
Google doesn’t always respect the title tags you set. They sometimes choose to display something slightly different.
The title tag is a great opportunity to write a headline which:
- includes the keyword you want the page to rank for, and
- is compelling enough to make searchers click and visit your site.
Conventional wisdom also suggests keeping yours under 60 characters to avoid truncation in full in search results. However, it’s not so much about the number of characters but rather pixels. Therefore, it’s a good idea to use a SERP pixel tool to make sure your titles don’t get cut.
Meta descriptions are also important, mainly because they too can affect the click-through rate.
SIDENOTE.
Click-through rate is not thought to be a direct ranking factor, but it does directly affect how much traffic you get from search.
If you want to avoid the risk of truncation, your meta descriptions should not exceed ~155 characters. Use the pixel tool mentioned above to keep them within limits.
Recommended reading: How to Craft the Perfect SEO Title Tag (Our 4-Step Process)
d) Use headers and subheaders to create a logical structure
Use the standard HTML format for headers (H1 to H6) to make it easy for search engines to understand the structure of your page and the importance of each section.
Header 1 should be reserved for the on‐page title of your content and should ideally include the main keyword (or something closely related to the main keyword) that you’re targeting. You can have more than one H1 tag per page, but we recommend sticking to one.
Header 2 should be used for the titles of the main sections on your page. They should also include the main keyword you’re targeting (whenever possible and natural—don’t shoehorn!) and are a good place to add additional (longer‐tail) keywords for which you want to rank.
Every time you go a step deeper in your content, use the next type of header, e.g., Header 3 for subheadings within an H2 section, and so on.
Here’s what a well‐structured piece of content looks like:
- H1: The Complete First-Time Traveller’s Guide to Dublin
- H2: Sights & Attractions
- H3: Trinity College
- H4: The Book of Kells Exhibition & Old Library
- H3: The Guinness Storehouse
- H4: The Gravity Bar
- H3: The Temple Bar Area
- H3: Trinity College
- H2: Accommodation
- H3: Hotel 1
- H3: Hotel 2
- H3: Hotel 3
- H2: Restaurants
- H3: Upscale restaurant
- H3: Gastropub
- H3: Another hip place
- H2: Bars
- H3: Bar with live music
- H3: Bar with great cocktails
- H3: Very touristy bar
- H2: Conclusion
- H2: Sights & Attractions
Following a clear and exhaustive structure makes it easy for search engines to categorize your content and also helps human readers.
e) Optimize your images
Images are great for humans, but search engines can struggle to make sense of them.
To illustrate that point, here’s what happens when you upload a photo of butter to Google’s Cloud Vision API—their machine‐learning image identification tool:
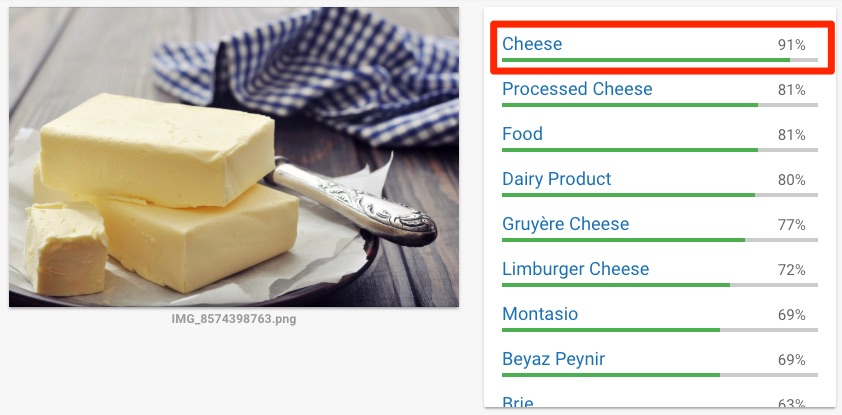
Google is 91% sure that this is a photo of cheese, which is wrong.
To help Google (and other search engines) understand your images, you should use the alt tag to describe and explain them. In this case, a good alt tag would be alt=”Butter”.
In WordPress, editing the alt tag is done by using the Alternative Text field in the image editor:
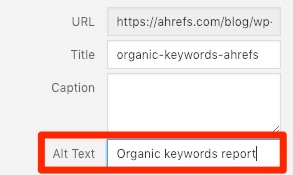
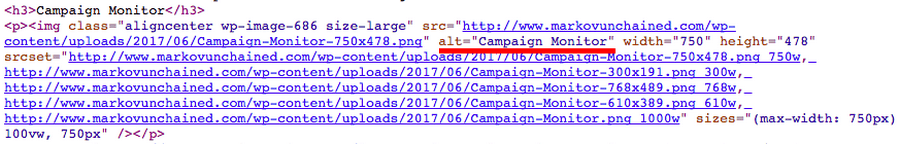
If you’re not using WordPress, you can also add the tag manually:
f) Set up Schema
Schema has become a popular way to improve how your website looks in search results. For example, you can use it to add ratings to your search results entry, thus making it more noticeable:
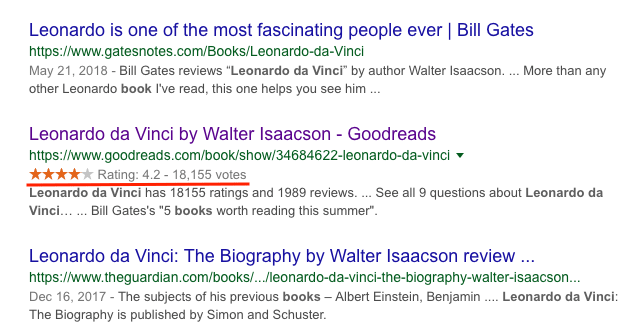
To get started with using Schema, you should check out the official documentation and these tools that allow you to generate and test structured data.
Learn more about on-page SEO
On-page SEO is a complex beast. Everything above will get you off on the right foot, but there’s always more to learn (as is the case with everything SEO-related)
Check out our full guide to on-page SEO to learn more.
Chapter 3: How to Increase Blog Traffic Now
Would you like to increase your blog traffic? It’s important to know and understand SEO (search engine optimization); however, it’s imperative to provide visitors with quality, unique content that will benefit them — it solves their problems. Follow the five SEO steps below to increase your blog traffic today and your web traffic will increase.
Blog Traffic: 5 SEO Tips to Increase Your Web Traffic Today

Select the right ‘targeted’ keywords and phrases.
You’ve heard and read many times how it’s important to select the ‘right’ keywords and phrases for your blog/website. You can use a popular keyword research tool to discover the keywords that will work for your website.
Once you have your keywords/phrases, it’s important to use one primary keyword/phrase and two ‘secondary’ keywords/phrases throughout a text, so it looks good on academized reviews. If you do this, your blog traffic will increase.
It’s important to remember NOT to stuff your blog post with keywords/phrases. Keyword density should not exceed 5%. The ideal keyword density is 2% – 5% — anything over this begins to look like spam content.
Images need alt tags and text descriptions.
Do you enter an alt tag for an image that accompanies a blog post? If you don’t, you’re missing out on an SEO opportunity that could increase your blog traffic.
Tip: Review alt tags to make sure you’re using the right keywords/phrases that will increase your blog traffic.
Your alt tag should incorporate your keywords/phrases. Also, write a ‘text description’ and caption for your images that includes your keywords/phrases.
Quality link building.
It’s important to have quality internal and external links, especially one-way links. A one-way link is when another blog is linked to yours, but you don’t link back to it. This is a good SEO strategy.
You may be tempted to purchase links as part of your link building strategy; however, you may not know the quality level of the links being purchased. It’s better to build links organically.
Tip: Check the links on your website because you don’t want to discover you have a ’404 Error.’ This happened to me, and I had to figure out ‘how to’ fix it.
Before you link to other blogs, make sure you ‘test’ the links. Broken links aren’t helpful to your visitors and it may deter them from visiting your blog. This will decrease your blog traffic.
Understanding how search engines work.
You may be a fan of G company (who isn’t), but there are other search engines, excite, and others If you don’t pay attention to these search engines algorithms, you’re missing an opportunity to increase your web traffic.
FYI: Companies encourage bloggers to submit their sitemaps on a daily basis or at least once a few times a week as a way to increase their search engine traffic.
The best SEO practices include understanding how other search engines index and rank blogs/websites. For example, G uses sitemaps to index blogs and websites. There are directories which allows users to submit their information manually. It’s reviewed by their editorial team. Once you understand how search engines are crawling and indexing your blog, you can adjust your SEO strategy and increase your blog traffic.
Providing quality content.
It’s important to keep search engine optimization in mind when you write your blog posts. However, it’s more important to write unique, quality content that attracts and converts visitors (if you’re monetizing your blog).
You can write web content that’s highly optimized. But if it’s not helpful to visitors, they’ll find other blogs that give them what they want.
As a freelance writer or ghost writer, you know ‘how to’ write and provide quality content. Learn all you can about SEO (search engine optimization) because the more you know, the more you can help your freelance writing clients improve their web content which will improve their blog traffic.